Noun Clause Examples : 😀 What is the noun clause in this sentence. Noun Clauses ... : (this noun clause is used as a subject complement) i must decide which english course to take.. Some examples of nouns include, man, house, and car. Biobots are changing how we think of robots. There are three types of subordinate, or independent, clauses: Relative clauses are dependent clauses that modify or give more information about a noun in the independent clause. For example (noun clauses shaded):
This creates the clause (a subject plus a verb). A noun clause is a clause that plays the role of a noun in a sentence. Relative clauses are dependent clauses that modify or give more information about a noun in the independent clause. This is only one example, as there are many different ways that noun clauses can be used. It can be the subject or the object of the verb.
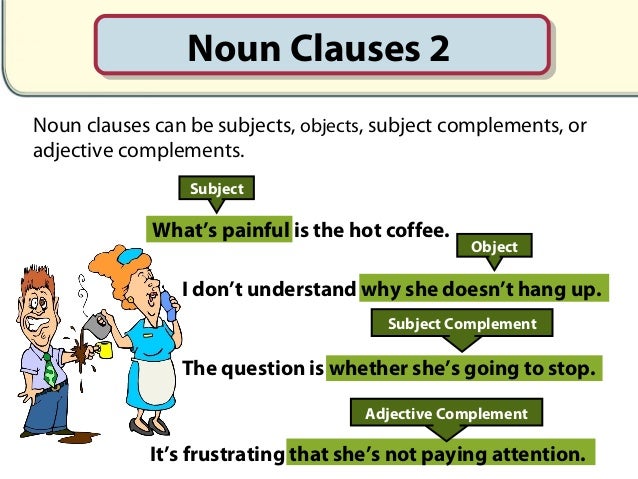
A noun clause is a clause that plays the role of a noun in a sentence.
Dependent clauses come in three types: Scar, who was simba's jealous and wicked uncle, threatened to take over pride rock. You must choose which flavor of ice cream you want. Noun clauses can function as subjects, objects, or complements. Biobots are changing how we think of robots. Moreover, a clause is defined as a unit of grammar that contains at least one verb and a subject. For example (noun clauses shaded): What is noun clause, example sentences; It can be the subject or the object of the verb. I like what i see. What is a noun clause? Below, you will see a regular yes/no question, followed by a related sentence that includes a noun clause. A noun clause is a clause that plays the role of a noun.
It can be the subject or the object of the verb. A noun clause has to do with the beta clause, which we also call a dependent or subordinate clause which performs the function of a noun in a sentence or functions like the nominal group. This is only one example, as there are many different ways that noun clauses can be used. A noun clause is a dependent clause that acts as a noun. I know that the students studied their assignment.

A noun clause cannot stand alone as a sentence because it cannot express a complete thought.
(this noun clause is the object of a preposition) by now it is becoming clear that lots of dependent signals introduce noun clauses. (like all clauses, a noun clause has a subject and a verb. We know that whatever you want is a clause because it has a subject (you) and a verb (want). A noun is a part of speech that names a person, place, or thing. You must choose which flavor of ice cream you want. A noun clause is a subordinate/dependent clause that generally comes after the main clause. Noun clauses replace subjects, objects, or subject complements in sentences. I want to know what all the fuss is about. what all the fuss is about, is the noun clause and functions in the sentence as the direct object of the verb know.. Noun clauses begin with words such as how, that, what, whatever, when, where, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whom, whomever, and why. Examples of noun clauses as the subject: In other words, the noun phrase does not stand alone as a complete concept. Biobots are changing how we think of robots. A noun clause is a dependent clause that acts as a noun.
It is usually linked to the main clause by these conjunctions: In the noun clause you said is a subject plus a verb. I know that the students studied their assignment. Noun clauses test 2 / answers. What is noun clause, example sentences;

Examples and definition of a noun clause.
That, which, what, who, whom, whose, where, why, when, how, if, whether, whatever, whichever, whoever, whomever, whenever, wherever, Noun clauses describe something about the verb or the sentence. We need to understand that in a sentence, a noun clause will be a dependent clause. A noun clause is a clause that plays the role of a noun in a sentence. Noun clauses begin with words such as how, that, what, whatever, when, where, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whom, whomever, and why. This means that the noun clause cannot stand by itself. Noun phrases generally begin with words such as how, that, what, whatever, when, where, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whom, whomever, and why. Noun clauses replace subjects, objects, or subject complements in sentences. The noun clause is acting as the object of the sentence. It can be used as the subject, direct object, indirect object, object of a preposition, subject complement, or appositive. There are instances wherein we would like to name something but a lone word would not suffice, and that is when we need a noun clause, which is composed of a group of words, in order to name something. It can be the subject of a sentence, an object, or a complement. The noun clause is a clause that functions like a noun in the sentence.